
Ahmed M. Amer & Mohamed M. EL-Hadi, Int. Journal of Computer Science & Mobile Computing, Vol.8 Issue.7, July- 2019, pg. 71-78
© 2019, IJCSMC All Rights Reserved 71
Available Online at www.ijcsmc.com
International Journal of Computer Science and Mobile Computing
A Monthly Journal of Computer Science and Information Technology
ISSN 2320–088X
IMPACT FACTOR: 6.199
IJCSMC, Vol. 8, Issue. 7, July 2019, pg.71 – 78
Tableau Big Data Visualization Tool in
the Higher Education Institutions for
Sustainable Development Goals
Ahmed M. Amer; Mohamed M. EL-Hadi
PhD. Candidate; Professor of Information Systems
ahmedmaeamer@gmail.com; mohamed.m.elhadi@gmail.com
Department of Computer Sciences and Information Systems
Sadat Academy for Management Sciences
Abstract— The purpose of this paper is to use of Tableau in HEIs to achieve the Sustainable Development
Goals (SDGs). Tableau can use large data sets to analyse, visualize and share knowledge, such as: whole
Egypt, HEIs, governorate, university, college, program, course, faculty members, and students to determine
the demography and performance. It provides a variety of graphs, chart forms and dashboards that can assist
to have a better tool in HEIs for sustainability. An analysis based on a literature review of visualization tools
such as Tableau and sustainable development goals. This paper suggests that most 17 SDGs and ESDGs can
be analysed, visualized and shared knowledge using Tableau. Tableau tool can be used to study the extent to
which higher education institutions can be used to contribute to the achievement of sustainable development
both internal and external EHEIs geographical boundaries. This paper emphasizes the application of a
relevant practical underpinning to support Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs).
Keywords— Big Data, Visualization Tools, Tableau; HEIs, SDGs.
I. INTRODUCTION
Headings Tableau is one of the tools of knowledge management systems for the third generation of the
Internet with live connection. In higher education, Tableau is unlocking the power of data to improve learning,
fundraising, planning, and research. Hundreds of leading institutions use Tableau to analyze student enrolment,
achievement, and demographics. Educational institutions are developing better alumni relations and
streamlining educational reporting. In the classroom and in the lab, Tableau enriches the learning experience
with analytics anyone can use and understand [1].
The role of HEIs in achieving sustainable development (SD) was highlighted for the first time in the 1972
Stockholm Declaration on the Human Environment [2]. Since then, HEIs and their stakeholders have
increasingly engaged in a number of global initiatives and expressed their commitment to SD in a variety of
national and international declarations and charters [3]. Recent examples include the United Nations Higher
Education Sustainability Initiative (UN HESI) and the UN Higher Education and Research for Sustainable
Development (HESD) platform. Both initiatives foster the implementation of the Sustainable Development
Goals (SDGs), as part of a globally agreed policy agenda for SD, in higher education [4] and [5].
Education for sustainable development (ESD) is expected both to make people more aware and better
qualified to take part in shaping future developments responsibly, and to raise their awareness of the problems
Ahmed M. Amer & Mohamed M. EL-Hadi, Int. Journal of Computer Science & Mobile Computing, Vol.8 Issue.7, July- 2019, pg. 71-78
© 2019, IJCSMC All Rights Reserved 72
related to sustainable development and bring forth innovative contributions to all economic, social,
environmental and cultural issues [6].
Universities play an important role for fostering ESD ‗by addressing sustainability through their major
functions of education, research and outreach‘ [7].
At the Millennium Summit of the United Nations in 2000, all UN members agreed to the eight
international development goals called the Millennium Development Goals (MDGs) of 2000-2015. To
continue and to complete what the MDGs did not achieve, the General Assembly of United Nations on
25 September 2015 adopted a resolution titled ―Transforming Our Word: the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable
Development‖, a plan of action for people, planet, and prosperity. They seek to balance the three dimensions
of sustainable development: the economic, social and environmental [8]. The resolution called all
countries and all stakeholders of governments, private sectors, academic communities, as well as civil
societies to act in collaborative partnership to implement all of 17 SDGs. [9].
II. BIG DATA VISUALIZATION TOOLS USED IN THE HEIS AND COMPARISON
The following are five big data visualization tools [12]:
A. QlikView
QlikView is a solution that focuses on the user as the receiver of data. It allows users to explore and discover
data in a workflow similar to the way developers work when processing data. To sustain flexibility in its
approach to data exploration and visualization, this software strives to maintain the association between data.
It‘s flexible. It allows setting and weak every little aspect of each object and customizes the look and feel of any
visualizations and dashboards. With such great deal of flexibility, there also comes an incorporated ETL
(Extract, Transform, and Load) Engine that enables you to conduct the ordinary data cleansing operations.
However, it may turn out to be costly. It has many unique features like patented technology and has in-memory
data processing, which executes the result very fast to the end users and stores the data in the report itself.
B. Klipfolio
Klipfolio is a BI solution that resides 100% in the cloud (no desktop application is required) providing an
insightful tool for data visualization and dashboard composition. It supports connectivity to a variety of data
sources, both online and offline. The online sources integrate a range of cloud-hosted storages including Google
Sheets, Relational DBs, and other services that provide data in all kinds of forms. It supports a great variety of
offline service types: MS Excel, CSV, XML, JSON, and others. It applies the principle of responsiveness to
facilitate the discovery of dashboards with the use of diverse technological platforms, from smartphones and
tablets, to desktop computers and smart TVs.
C. Tableau
Tableau provides facility to connect to a variety of data sources with many systematic types, such as data
systems organized in file formats (CSV, JSON, XML, MS Excel, etc.), relational and nonrelational data systems
(PostgreSQL, MySQL, SQL Server, MongoDB, etc.), cloud systems (AWS, Oracle Cloud, Google BigQuery,
Microsoft Azure). The core distinction from competitors is that Tableau has a special feature of Data Blending.
Another unique feature is the ability for collaboration in real time that makes it a valuable investment for
commercial and non-commercial organizations alike. There are several ways to share the reports in Tableau: by
publishing them to a Tableau server; via email Tableau Reader capability; by publishing Tableau workbook
openly and giving access to anyone who has a link. This magnitude of options enables great flexibility and
removes many restrictions. Tableau Public is a free software that connects any data source be it corporate Data
Warehouse, Microsoft Excel or web-based data, and creates data visualizations, maps, dashboards etc. with real-
time updates presenting on web. They can also be shared through social media or with the client.
D. Power BI
Power BI is the software solution, developed and supported by Microsoft, for business intelligence and
analytics needs. At the core of Power BI is an online service with various options for interaction, also featuring
several outlets for connection to data provided by third party software and services. In addition, it provides a
simple web-based interface with a plenitude of useful features varying from customizable visualization to
certainly limited controls of data sources. The desktop application expands the available functionality to an even
larger extent with the addition of tools for data cleansing and normalization. Also, it has connections to some
other software from the Microsoft‘s toolbelt but goes much farther than that by utilizing a whole suite of novel
business analytics tools. Thus, Power BI is not just related to other products; it is tightly integrated with the
main Microsoft tools including MS Excel, Azure Cloud Service, and SQL Server.
Ahmed M. Amer & Mohamed M. EL-Hadi, Int. Journal of Computer Science & Mobile Computing, Vol.8 Issue.7, July- 2019, pg. 71-78
© 2019, IJCSMC All Rights Reserved 73
E. Google Data Studio
The youngest tool on our list is a part of Google‘s analytics solutions — Google Data Studio. Being relatively
new to the field, it strives to take its position among many competitors via ease of usage, simple yet beautiful
design, innovative problem-solving, and straightforward, habitual ways to share dashboards (just as you usually
share documents).While still being in Beta, Google Data Studio gives an interesting insight into how it can
process the data. It is a fully web-based solution, and there is no desktop version (unlike other BI solutions). The
tool had a pretty decent start, but time will show whether it will perform well in the long run.
III. TABLEAU BENEFITS
The following are some of the benefits of Tableau [13]:
A. Ease of use
According to Gartner‘s Magic Quadrant, more than 70 percent of Tableau‘s customers selected the product
based on its ease of use for the business user. Tableau basics can be understood in a few hours.
B. Advanced Analytics
Tableau‘s client references ranked it in the bottom third of all Magic Quadrant vendors for complexity of
analysis.
C. Data Preparation
Despite efforts to improve its data preparation capabilities in version 9, Tableau still has weaknesses in the
area of data integration across data sources. Tableau supports a diverse range of data connectivity options put
offers little support when it comes to integrating combinations of these sources in preparation for analysis.
D. Security
With Tableau you can establish ―row level‖ security at the data level. In order to set up row level security in
Tableau, the user must have a database user account. The increased numbers of database accounts mean
increased opportunities for hackers.
E. Cost
Tableau costs less upfront than Qlikview. Not only does Tableau have a reputation as being less expensive to
purchase, it requires less developer involvement to implement, maintain and use making its total cost of
ownership over its lifetime less than Qlikview‘s.
IV. TABLEAU PRODUCTS
Tableau has five products which together form a product platform to enable users to create Tableau files.
These five products are: Tableau desktop, Tableau online, Tableau Server, Tableau Public, and Tableau reader.
[14].
A. Tableau Desktop
Tableau Desktop is a data visualization tool designed to create data visualization, report and dashboard in a
fast and intelligent way. To be more specific, users can connect to multiple data sources, carry out multi-
dimensional data analysis, create dashboards or report, modify metadata and publish a complete workbook to
Tableau server if needed.
B. Tableau Online
Tableau Online is a hosted version of Tableau Server. It is the business analytics platform where people can
share dashboards, interact with report and gain insights. It is hosted in the cloud so that there is no hardware, no
set-up time needed.
C. Tableau Server
Tableau Server is a data governance platform and can be either browser based or mobile based. It enables
users to publish dashboards on Tableau Server so that everyone in the organization can share, collaborate and
interact with them. It facilitates the integration of data in the organization.
D. Tableau Public
Tableau is a free tool that anyone can use to connect to data, create interactive data visualizations and publish
them on the web. Since everyone has access to published data, user should be careful not to put the proprietary
data on Tableau Public.

Ahmed M. Amer & Mohamed M. EL-Hadi, Int. Journal of Computer Science & Mobile Computing, Vol.8 Issue.7, July- 2019, pg. 71-78
© 2019, IJCSMC All Rights Reserved 74
E. Tableau Reader
Tableau Reader is a free desktop application that users can open and interact with data visualizations which
are created with Tableau Desktop.
V. TABLEAU ARCHITECTURE
Tableau has highly scalable and it has n-tier client-server based architecture that serves the
mobile clients, web clients, and desktop installed software [15] and [16].
Figure 1: Tableau Architecture for Sustainable Development
Tableau server is an enterprise business class platform it can set up hundreds of thousands
of users. It offers powerful mobile and web-based analytic works with companies existing
data and security protocol.
Scales up: Is multi-threaded
Scales out: Is multi-process enabled
Provides integrated clustering
Supports High Availability
Is secure
Runs on both physical and Virtual Machines
Figure 2: Tableau Server Architecture [15]
Data Layer: The basic characteristic of tableau that supports your choice of data architecture. Tableau does
not require any restrictions for the database like data to be stored in any single system. Most of the
organizations have a heterogeneous environment. Tableau can work with all these simultaneously.
Data Connectors: Tableau includes a number of optimized data connectors for databases such as Microsoft
Excel, SQL Server, Oracle, Teradata, Vertica, Cloudera Hadoop, and much more. There is also a generic
ODBC connector for any systems without a native connector. Tableau provides two modes for interacting
with data: Live connection or In-memory. Users can switch between a live and in-memory connection as
they choose.
Ahmed M. Amer & Mohamed M. EL-Hadi, Int. Journal of Computer Science & Mobile Computing, Vol.8 Issue.7, July- 2019, pg. 71-78
© 2019, IJCSMC All Rights Reserved 75
Live connection: Tableau‘s data connectors leverage your existing data by sending dynamic SQL or MDX
statements directly to the source database rather than importing all the data. It‘s the front-end analytics
client to many of the largest databases in the world. Tableau has optimized each connector to take
advantage of the unique characteristics of each data source.
In-memory: Tableau offers a fast analytic performance due to in-memory data engine. Data engine will
extract the data and bring it in memory in the tableau. Data engine utilized your entire system to get the fast
query response one million of rows of data. Data engine can access the disk store as well as RAM and
cache memory.
Application Server: Application server provides the authorization and authentications from the database.
VIZ sql server: VIZ sql server converts the sql queries into visualization.
Data Server: data server centrally manage and store tableau data sources. It also maintains Metadata from
tableau desktop such as calculations, definition, and groups.
Backgrounder: The backgrounder refreshes scheduled extracts and manages other background tasks.
Gateway/ Load Balancer: It is the primary Tableau Server which trails requests to other components.
Requests which come in from the client firstly strike the gateway server and then routed to the appropriate
procedures. If multiple procedures are configured for any component, the Gateway will work as a load
balancer and share the requests to the procedures. In a single server configuration, every procedure sits on
the Gateway, or primary server. When running in a distributed atmosphere, one physical machine is
designated the primary server and the others are designated as worker servers which can run any number of
other procedure. Tableau Server always uses only one machine as the primary server.
Clients (Web Browsers and Mobile Apps): It offers interactive dashboards toward clients using zero-
footprint HTML and JavaScript (AJAX) in a web browser, or natively through a mobile app. No plug-ins or
helper applications are necessary. Tableau Server supports:
Web browsers: Internet Explorer, Firefox, Chrome and Safari.
Mobile Safari: Touch-optimized views are automatically served on mobile Safari.
iPad app: Native iPad application that provides touch-optimized views and content browsing.
Android app: Native Android application that provides touch-optimized views and content browsing.
Android browser: Touch-optimized views are automatically offered in the Android browser.
Clients (Tableau Desktop): Tableau Desktop is the rapid-fire authoring environment used to generate and
publish sights, reports and dashboards to Tableau Server. Using this, a report author can tie with multiple
data sources, explore relationships, create dashboards, modify metadata, and finally issue a completed
workbook or data source to Tableau Server.
VI. SDGS OF THE UNITED NATIONS
The 17 Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) are the world's best plan to build a better
world for people and our planet by 2030. Adopted by all United Nations Member States in
2015, the SDGs are a call for action by all countries - poor, rich and middle-income - to
promote prosperity while protecting the environment. They recognize that ending poverty
must go hand-in-hand with strategies that build economic growth and address a range of
social needs including education, health, equality and job opportunities, while tackling
climate change and working to preserve our ocean and forests. The Sustainable Development
Goals (SDGs), otherwise known as the Global Goals, are a universal call to action to end
poverty, protect the planet, and ensure that all people enjoy peace and prosperity [17]. It is
made up of 17 goals meant to be applied to every country, not just developing nations.
The sustainable development goals are [8]:
Goal 1. End poverty in all its forms everywhere.
Goal 2. End hunger, achieve food security and improved nutrition and promote sustainable agriculture.
Goal 3. Ensure healthy lives and promote well-being for all at all ages.
Goal 4. Ensure inclusive and equitable quality education and promote lifelong learning opportunities for all.
Goal 5. Achieve gender equality and empower all women and girls.
Goal 6. Ensure availability and sustainable management of water and sanitation for all.
Goal 7. Ensure access to affordable, reliable, sustainable and modern energy for all.
Goal 8. Promote sustained, inclusive and sustainable economic growth, full and productive. employment
and decent work for all.
Goal 9. Build resilient infrastructure, promote inclusive and sustainable industrialization and foster
innovation.
Goal 10. Reduce inequality within and among countries.
Goal 11. Make cities and human settlements inclusive, safe, resilient and sustainable.
Ahmed M. Amer & Mohamed M. EL-Hadi, Int. Journal of Computer Science & Mobile Computing, Vol.8 Issue.7, July- 2019, pg. 71-78
© 2019, IJCSMC All Rights Reserved 76
Goal 12. Ensure sustainable consumption and production patterns.
Goal 13. Take urgent action to combat climate change and its impacts.
Goal 14. Conserve and sustainably use the oceans, seas and marine resources for sustainable development.
Goal 15. Protect, restore and promote sustainable use of terrestrial ecosystems, sustainably. manage forests,
combat desertification, and halt and reverse land degradation and halt biodiversity loss.
Goal 16. Promote peaceful and inclusive societies for sustainable development, provide access to justice for
all and build effective, accountable and inclusive institutions at all levels.
Goal 17. Strengthen the means of implementation and revitalize the global partnership for sustainable
development.
Where companies can choose just one SDG they wish to address in their operations.
Similarly, The Higher Education Sustainability Initiative (HESI) asks colleges and
universities to pick one of the SDG they wish to contribute towards [17].
Target 4.7 by 2030, ensure all learners acquire knowledge and skills needed to promote sustainable
development, including among others through education for sustainable development and sustainable lifestyles,
human rights, gender equality, promotion of a culture of peace and nonviolence, global citizenship, and
appreciation of cultural diversity and of culture‘s contribution to sustainable development. SDG 4.7.1, Extent to
which (i) global citizenship education and (ii) education for sustainable development, including gender equality
and human rights, are mainstreamed at all levels in: (i) national education policies, (ii) curricula, (iii) teacher
education and (iv) student assessment. [18].
VII. THE SUSTAINABLE DEVELOPMENT GOALS (SDGS) IN EGYPT
In line with the 2030 Agenda, the Egyptian Government has launched a working plan
called Egypt‘s Vision 2030, also known as Sustainable Development Strategy (SDS), which
encompasses the economic, social and environmental dimensions of development. SDS
promotes economic flourishing based on justice, social integrity and participation. It is under
the SDS that all development plans in Egypt are incorporated while at the same time being
strongly guided by the SDGs. Additionally, in an effort to monitor the implementation and
reporting on progress of the SDGs, the Primer Minister appointed the Ministry of Planning,
Monitoring and Administrative Reform (MoPMAR) as its Rapporteur. The ministry is
responsible for coordinating the steps towards integrating, institutionalizing and
implementing the SDGs.
Key Messages of Egypt Voluntary National Review 2018
Egypt is committed to progress towards achieving the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). Egypt‘s
Sustainable Development Strategy, Egypt Vision 2030, is in line with SDGs. The national strategic plan‘s
three dimensions (economic, social and environmental) are based on ten pillars covering broadly the SDGs.
The plan provides programs, policies and measurable indicators in order to put Egypt on the right path
toward sustainable development.
Egypt embarked on a very comprehensive and home grown economic reform program that is supported by
the international financial institutions staring November 2016. The Government of Egypt took very bold
and timely measures as well as overdue reforms to put the economy on the path towards a more stable
resilient economy. After a challenging year, economic fundamentals are stabilizing with reduction in fiscal
deficit, curbing in the rate of inflation, waning in external deficit and increasing in the growth rate of
output; all of these are met with increased confidence from domestic and international investors. The
Government of Egypt is committed to pursuing its agenda of economic reforms to create an enabling
environment for inclusive growth and sustainable development.
Egypt is mindful of the vulnerable groups who are likely more adversely affected by stabilization and
reform programs. In order not to leave anyone behind, the Government of Egypt has scaled up its social
protection programs and has improved their target mechanisms. In addition, the Government of Egypt is
allocating more resources to the more deprived areas to provide better quality of public services and
infrastructure.
Egypt is pursuing an ambitious plan to upgrade its infrastructure across all sectors and all regions within the
country. The energy sector witnessed a substantial upgrade in its capacity to produce, transport and
distribute electricity. Egypt increased its capacity to produce electricity by at least 15 Gigawatt of electricity
using very advanced, sustainable and efficient technologies. Indeed, the energy strategy aims at increasing
the share of the renewable energy to reach 42% by 2035. The government has also enacted major reforms in
the legal framework of its electricity sector opening the door for increased participation of the private sector
Ahmed M. Amer & Mohamed M. EL-Hadi, Int. Journal of Computer Science & Mobile Computing, Vol.8 Issue.7, July- 2019, pg. 71-78
© 2019, IJCSMC All Rights Reserved 77
and effective regulatory role of the state. All of these efforts in the energy sector are consistent with Egypt‘s
vision to become the energy hub of the Eastern Mediterranean.
Egyptian network of highways witnessed major extensions and improvements. The national highway
project is a much needed project to link distant parts of Egypt beyond the main cities and the Nile Valley in
order to create economic opportunities and to expand beyond the narrow valley.
The growing population consisting mainly of youth represents both a challenge and an opportunity. It is a
challenge since the government needs to continuously scaling up the country‘s infrastructure and housing
units especially for low income groups. This explains Egypt‘s heavy investment in infrastructure projects as
well as social housing projects. On the other hand, this young sizeable population would be an asset if these
young people obtain adequate quality education and training that prepare them for the fourth industrial
revolution.
Water scarcity within Egypt and regionally is a key challenge for the growing population; especially that
the agricultural sector consumes almost two thirds of its supply of fresh water. Ensuring sustainable water
resource management is a matter of high priority to the Government of Egypt.
Egypt‘s Vision 2030 and the 2030 Agenda are implemented by engaging all stakeholders. The role of the
private sector and the civil society is key in the realization of these goals. The inclusivity and
transformability aspects of the 2030 Agenda and its national counterpart necessitate active contribution of
the private sector and the civil society in the achievement of all the goals. The Government of Egypt
awareness this fact and is capitalizing on the positive synergies between the governmental efforts, private
sector efforts and civil society efforts to achieve this ambitious agenda.
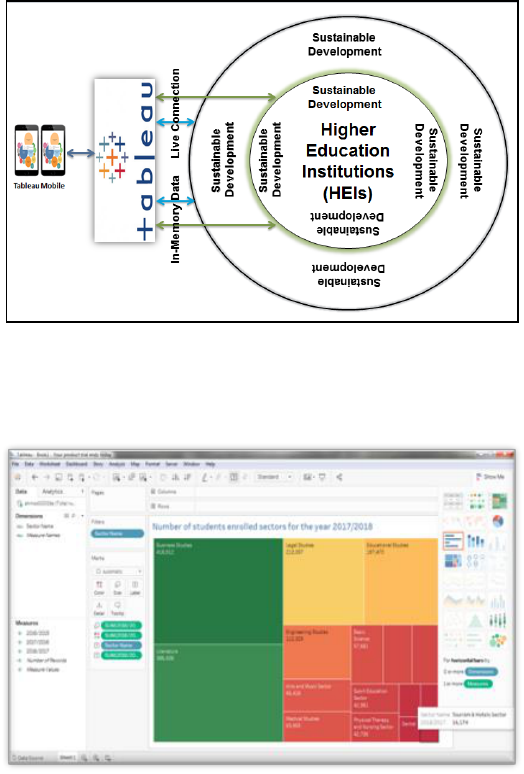
VIII. TABLEAU IN THE HEIS FOR THE SDGS
The Figure 4 is as shown in the Tableau in the HEIs for the SDGs
Figure 4: Tableau in the HEIs for the SDGs
An example of the charts is as shown in the Figure 5 in the Tableau. The different ratio of sectors can be
observed.
Figure 5: Number of students enrolled sectors for the year 2017/2018
Ahmed M. Amer & Mohamed M. EL-Hadi, Int. Journal of Computer Science & Mobile Computing, Vol.8 Issue.7, July- 2019, pg. 71-78
© 2019, IJCSMC All Rights Reserved 78
IX. CONCLUSIONS
Tableau is one of the top powerful and fastest growing data visualization tool used in HEIs.
Higher education for sustainable development is not foregrounded precisely. The only SDG of higher education
is SDG 4.7: ―By 2030, ensure all learners acquire knowledge and skills needed to promote sustainable
development, including among others through education for sustainable development and sustainable lifestyles,
human rights, gender equality, promotion of a culture of peace and non-violence, global citizenship, and
appreciation of cultural diversity and of culture‘s contribution to sustainable development‖.
The task of higher education institutions is to graduate people in different sectors who are able to achieve the
goals of different sustainable development.
The dimensions of sustainable development should not be limited to the three environmental, economic and
social dimensions, but must include, in accordance with the environmental approach, other environments such
as: higher education, politics, management, cultural, security, Industrial and tourism.
Using the Tableau data visualization tool should not be limited to analytics on target 4.7 but on all sectors.
The higher education sectors should include all aspects of the environmental approach...
REFERENCES
[1] Tableau, (2019). Tableau for Higher Education. Retrieved from https://www.tableau.com/solutions/education-higher-
ed-analytics
[2] UN, (2018a). Declaration of the United Nations Conference on the Human Environment. Retrieved from
http://www.un-documents.net/unchedec.htm
[3] Lozano, R., Lukman, R., Lozano, F.J., Huisingh, D., Lambrechts, W., (2013). Declarations for Sustainability in Higher
Education: Becoming Better Leaders, through Addressing the University System. J. Clean. Prod. 48, 10–19.
[4] UN, (2018b). Higher Education and Research for Sustainable Development (Hesd). Retrieved from
https://sustainabledevelopment.un.org/partnership/?p=11748
[5] UN, (2018c). Higher Education Sustainability Initiative (Hesi). Retrieved from https://
sustainabledevelopment.un.org/sdinaction/hesi
[6] Barth, M., Rieckmann, M. (2016). State of the art in research on higher education for sustainable development, in:
Barth. Routledge Handbook of Higher Education for Sustainable Development, London, 100 – 113. Retrieved from
http://www.academia.edu/17998746/State_of_the_Art_in_Research_on_Higher_Education_for_Sustainable_Develop
ment
[7] Fadeeva, Z.; Mochizuki, Y. (2010). Higher education for today and tomorrow: university appraisal for diversity
innovation and change towards sustainable development. In: Sustainability Science 5 (2), 249–256. Retrieved from
https://link.springer.com/content/pdf/10.1007%2Fs11625-010-0106-0.pdf
[8] UN, (2015). Transforming our world: the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development. Retrieved from
https://sustainabledevelopment.un.org/post2015/transformingourworld
[9] Ridho, T. K., Vinichenko, M., & Makushkin, S. (2018). Participation of Companies in Emerging Markets to the
Sustainable Development Goals (SDGS). Paper presented at the 741-752. Retrieved from
https://search.proquest.com/docview/2139001802?accountid=30906
[10] Clugston, R. M., & Calder, W. (1999). Critical dimensions of sustainability in higher education. In W. L. Filho (Ed.),
Sustainability and university life (pp. 31-46). New York: Peter Lang. Retrieved from
https://redcampussustentable.cl/wp-content/uploads/2018/03/3-Critical_dimensions_SHE.pdf
[11] SDSEGYPT2030, (2016). Sustainable Development Strategy: Egypt‘s Vision 2030. Retrieved from
http://sdsegypt2030.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/08/English-Booklet-2030.compressed.pdf
[12] Bobriakov, I. (2018).A Comparative Analysis of Top 6 BI and Data Visualization Tools in 2018. Retrieved from
https://medium.com/activewizards-machine-learning-company/a-comparative-analysis-of-top-6-bi-and-data-
visualization-tools-in-2018-658490665973
[13] Akscellenceinfo, (2017). Market for BI & Data Analytics. Retrieved from
http://www.akscellenceinfo.com/media/1090/market-for-bi-data-analytics.pdf
[14] Machairidou, S. (2018). Big Data and Tableau. Retrieved from https://ikee.lib.auth.gr/record/297918/files/GRI-2018-
21585.pdf
[15] Intellipaat, (2019). Tableau Architecture. Retrieved from https://intellipaat.com/tutorial/tableau-tutorial/tableau-
architecture/
[16] ABC Learn, (2018). Tableau Architecture. Retrieved from https://www.abclearn.com/courses/tableau/tableau-
basics/tableau-architecture/
[17] UN, (2017). Sustainable Development Knowledge Platform. Retrieved from
https://sustainabledevelopment.un.org/content/documents/3949ola.pdf
[18] UNESCO Institute for Statistics, (2018). Quick Guide to Education Indicators for SDG 4. Retrieved from
http://uis.unesco.org/sites/default/files/documents/quick-guide-education-indicators-sdg4-2018-en.pdf
